This is the era of social media. It binds us together in a vast, intricate network of global interactions. It is also place where businesses face a critical choice in their use of artificial intelligence (AI).
The decision businesses have at hand is whether to merely satisfy current legal benchmarks or to adopt a more comprehensive approach and principles in their AI practices. The impact of AI, amplified by social media, can influence public opinion, shape social dynamics, and even sway political landscapes. One wrong move and your brand might be forever tainted in the public sphere.
It’s imperative that businesses strive not only to meet legal standards but also to ensure their AI technologies are ethically grounded, accountable for their actions, and sustainable over time, fostering a positive influence in our interconnected society.
The Current Ethical Landscape of AI
In 2024, the ethical landscape of artificial intelligence (AI) continues to evolve rapidly. In the United States, there is a notable shift toward concrete regulatory action, underscored most recently by President Biden’s executive order aimed at fostering transparency and establishing new standards for AI. This order signifies a tailored approach to AI policy, promoting industry-friendly practices while encouraging sector-specific regulations.
Meanwhile, Europe has taken significant strides with the introduction of the AI Act, the world’s inaugural comprehensive AI legislation. This groundbreaking law, set to be implemented swiftly following its official approval, will impose bans on certain AI uses and mandate greater transparency and accountability for high-risk AI applications.
These regulations are designed to ensure that AI technologies are developed and deployed in a manner that is safe, transparent, and non-discriminatory, aligning with broader societal values and ethical norms. Europe’s proactive regulatory measures serve as a model for global AI governance, potentially shaping the development and regulation of AI technologies across the globe.
For businesses and organizations, these regulatory landscapes in the US and Europe underscore the urgency of navigating the ethical dimensions of AI with foresight and responsibility. As AI continues to transform industries and societal norms, adapting to these changes by implementing practices that uphold not only legal compliance but also ethical principles becomes imperative.
To seamlessly transition your organization’s approach to integrating artificial intelligence, consider adopting the LEAD framework, a comprehensive strategy that ensures your AI practices are not only legally compliant but also ethically sound, accountable, and durable for the long term.
Implementing the LEAD Framework in Business
The LEAD framework emerges as a comprehensive model for ethical AI, advocating for practices that are:
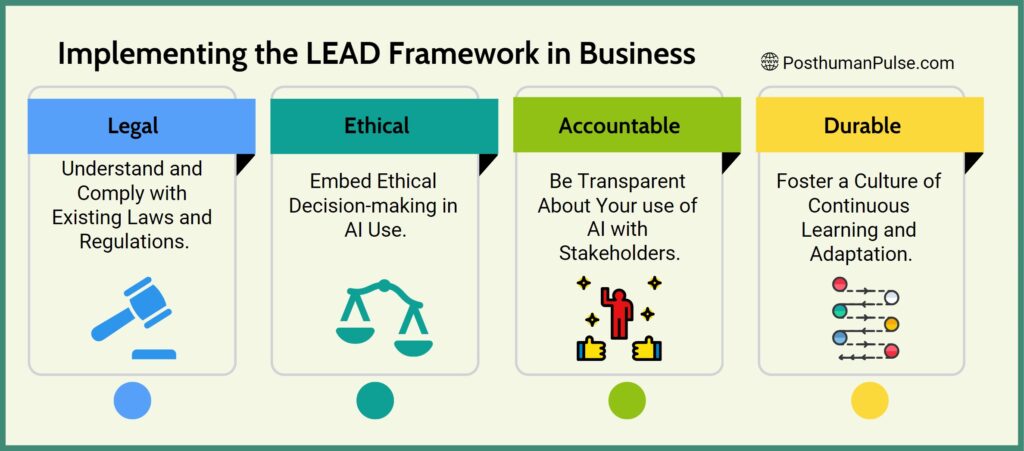
- Legal (L) – Understand and Comply with AI Regulations: Stay informed about the legal landscape surrounding AI use in your industry. Ensure that any AI tool or system you integrate into your business practices complies with existing laws and regulations.
This might involve consulting with legal experts to understand the implications of AI technologies and how they align with data protection, privacy laws, and industry-specific regulations. - Ethical (E) – Ethical Decision-Making in AI Use: Embed ethical decision-making in your use of AI by ensuring that the AI systems you employ are designed and used in a manner that respects ethical standards.
This includes using AI in ways that respect customer privacy, avoid bias, and promote fairness. You might conduct ethical reviews of AI tools before deployment and establish guidelines for ethical AI use within your business practices. - Accountable (A) – Foster Accountability and Transparency: Be transparent about your use of AI with stakeholders, including customers, employees, and partners. Communicate the purposes for which AI is used, and be accountable for its impacts.
Implement mechanisms for feedback and redress if AI systems cause unintended consequences, ensuring there’s a clear process for addressing concerns and mitigating any negative outcomes. - Durable (D) – Ensure Durability through Continuous Learning and Adaptation: AI technologies and societal expectations evolve, so it’s crucial to foster a culture of continuous learning and adaptation in your organization. Regularly review and update your AI strategies to incorporate new insights, technologies, and best practices.
This could involve training for your team on the latest AI trends and ethical considerations, as well as periodically reassessing the AI tools you use to ensure they remain aligned with your business values and societal norms.
Why Dropping ‘E’ is Not an Option: The Perils of being a LAD
Neglecting the ‘Ethical’ component in AI implementation can significantly impact businesses. Here are five potential consequences for businesses that choose to prioritize Legal, Accountable, and Durable aspects of AI use without integrating Ethical considerations (LAD), highlighting the importance of maintaining a comprehensive approach to AI integration:
- Reputational Damage: Businesses that fail to consider the ethical implications of their AI systems may face public backlash if their practices are perceived as harmful or unfair.
Negative public perception can lead to a loss of customer trust, which is difficult and costly to rebuild. The reputational damage can also deter potential partners and investors who prioritize ethical considerations in their business engagements. - Legal and Regulatory Risks: While a company might initially comply with current laws, ethical oversights can lead to future legal challenges as regulations evolve to address new ethical concerns.
Businesses that have not incorporated ethical considerations into their AI practices may find themselves scrambling to meet new standards, facing potential legal penalties, and incurring significant costs to retrofit compliance into existing systems. - Market Disadvantages: Companies that ignore ethical AI practices may find themselves at a competitive disadvantage. Consumers and businesses are increasingly valuing ethical considerations in their purchasing and partnership decisions.
Companies that proactively address these concerns can differentiate themselves in the market, attracting customers and partners who prioritize ethical considerations. - Operational Inefficiencies: Without ethical guidelines, AI systems may inadvertently perpetuate biases or operate in ways that are not aligned with the best interests of the company or its stakeholders.
These issues can lead to operational inefficiencies, as resources may need to be diverted to address problems that could have been avoided with a more ethical approach to AI development and implementation. - Innovation Stifling: Ethical oversights can stifle innovation by creating an environment where AI is developed in a vacuum without considering its broader impacts on society.
By incorporating ethical considerations, businesses can ensure that their AI innovations are not only technically advanced but also socially responsible, fostering an environment that encourages holistic and sustainable innovation.
As AI continues to redefine the boundaries of possibility, leading with ethics is not merely a choice but a necessity for businesses seeking to innovate responsibly.
The LEAD framework offers a blueprint for embedding ethical considerations into AI strategies, ensuring that technological advancements serve the greater good.
By embracing this comprehensive approach, businesses can navigate the ethical complexities of AI, transforming potential challenges into opportunities for sustainable growth and societal contribution.

